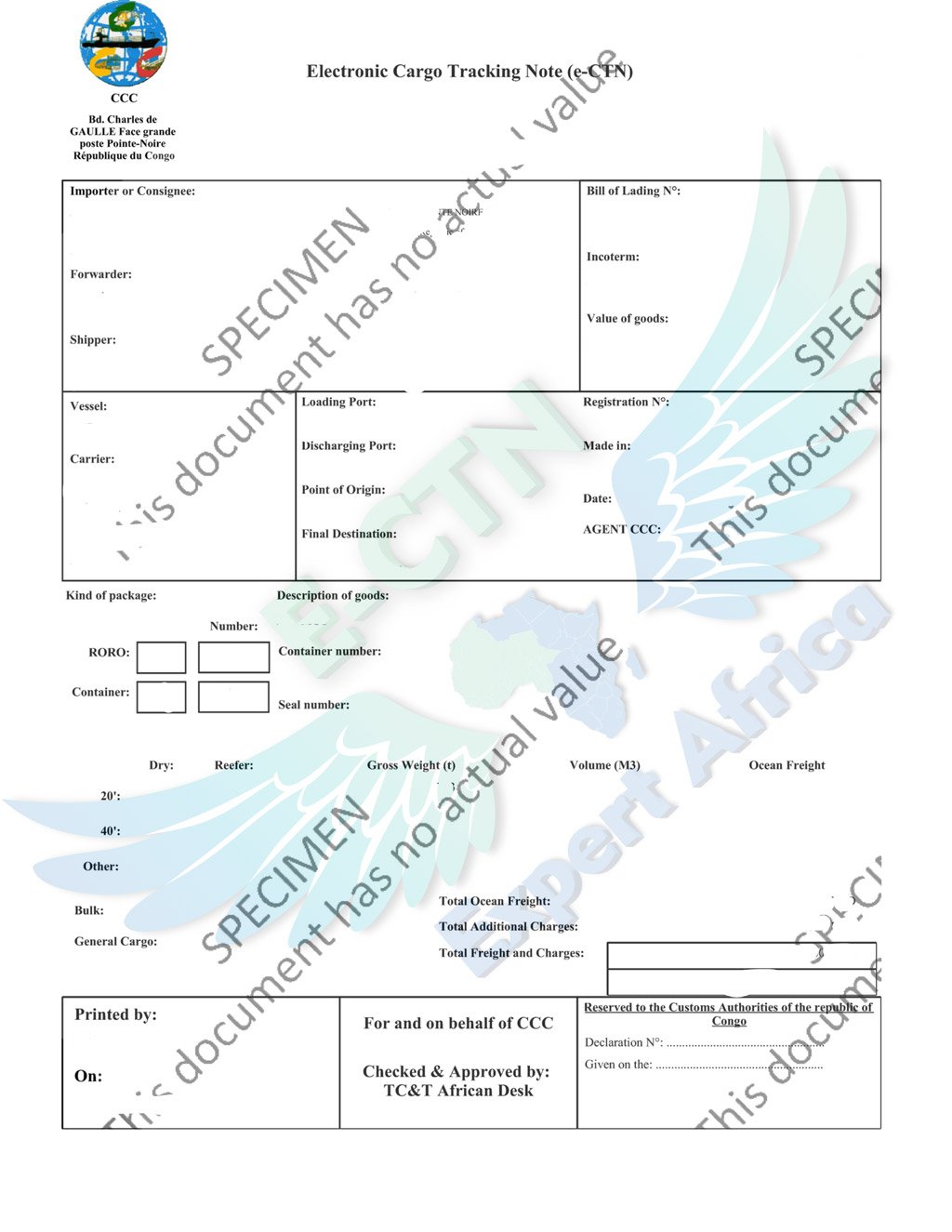
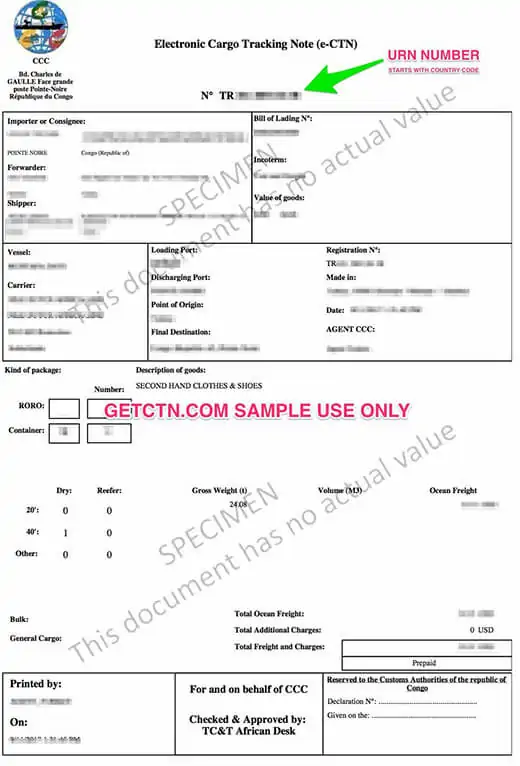
You must validate the ECTN before the 5th day after the departure at the latest. But it is suggested to validate the certificate before the vessel departs. If it is not validated it in the given time, the cost of the certificate will be 50% higher. If the ship arrives without a certificate, you will face a fine, equivalent to the value of the certificate plus the regulation charges determined by the authorities. And on top of that, your shipment will not have an entry clearance.
Certificate cost depends on the number of Bill of Ladings and the containers, the country of origin, the port of discharge, etc. This is why we can’t give you an exact price for the CTN. But if you share your shipment’s details with us we can provide you the best charges for your certificate. We offer free quotation.